Microbiology is the field of science that studies microscopic living organisms as well as viruses and prions. Microbiology and medical microbiology in particular are closely related to immunology since many pathogenic microbes generate immune responses in humans. Other subspecialties of microbiology include virology, the study of viruses;
Pages
▼
Electron Beam Scanners
Electron beam tomography (EBT) is a specialized form of computed tomography that is designed to obtain better images of heart structures than can be obtained using standard CT technology. In order to capture clear, accurate images of the constantly-moving heart, a CT’s X-ray source point must move extremely rapidly around the patient. In conventional CTs, X-ray tubes spin mechanically around the patient, but simply cannot move quickly enough to prevent blurring of cardiac images.
New Developments in Mammography/Elastography
Elastography is a new technique that uses ultrasound to assess the relative stiffness of different tissues. Adding a fourth dimension—time—to ultrasounds allows the movement and elasticity of normal tissue to be compared to the movement of lesions within the tissue. Because malignancies tend to be harder than normal tissue, stiffness is a promising diagnostic indicator.
St. Jude Medical Equipment
St. Jude Medical is a leading producer of medical technology and services for cardiology, neurology and chronic pain management practitioners and patients throughout the world. Founded in 1976, the company is based in St. Paul, Minnesota and has over 16,000 employees. St. Jude Medical develops advanced technologies with the aim of reducing medical costs while providing excellent patient care.
Siemens AG medical equipment
Cardio MRI Developments
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a technology for imaging the heart and its blood vessels that is based on magnet fields and radio frequency. As radio waves pass through a magnetic field generated by the electromagnet within the MRI, they align the protons within the nuclei of hydrogen atoms and generate signals that are detected by the coils that surround the patient.
Clinical Engineering
 Clinical engineering is a multidisciplinary field that requires excellent problem-solving skills and the ability to work with complex technologies and human factors. Clinical engineers apply both simple and highly sophisticated medical technology to improving healthcare delivery. As practical engineers who are present and active at the front line of the use of medical technology as well as knowledgeable in product design, they serve as a valuable bridge and conduit of information between biomedical engineers and practitioners.
Clinical engineering is a multidisciplinary field that requires excellent problem-solving skills and the ability to work with complex technologies and human factors. Clinical engineers apply both simple and highly sophisticated medical technology to improving healthcare delivery. As practical engineers who are present and active at the front line of the use of medical technology as well as knowledgeable in product design, they serve as a valuable bridge and conduit of information between biomedical engineers and practitioners.Pulmonary Medicine
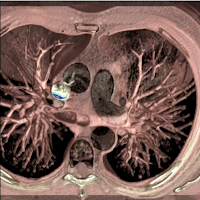
Pulmonary physicians, also known as pulmonologists, are internists that focuses on disorders of the respiratory tract. Pulmonologists deal with diseases and conditions that affect the lungs, focusing on their causes and prevention. They diagnose and treat patients and manage chronic diseases. Pulmonologists also manage mechanical ventilation for patients who need life support. Training in pulmonologists entails a two year fellowship following residency in internal medicine. Many physicians choose to study critical care medicine or sleep medicine in conjunction with pulmonology.